Pyrometry
- contactless measuring of surface temperatures
- easiest way of measuring moving parts
- no mechanical wearout
- fast reaction
- no measuring error by heat conduction
Contactless temperature measurement
The use of radiation pyrometer often is the simplest method to measure the temperature of surfaces. The typical disadvantages of contact sensors, like mistakes in discharge, wearout- and time delay, disappear by the contactless temperature measurement. Nevertheless some principles are to observe. The essential selection criterias for a radiation pyromter is the spectral range and the size of the measuring spot.
De facto, the most often used readings recorder are partial radiation pyrometers in long-wave spectral range of 8 … 14µm or short-wave in strait partial areas of 0.7 … 3µm. Special ranges for the measuring of glass are by 5.14µm.
Metallic surfaces show a good emission in the short-wave IR-range, while nonmetallic surfaces in long-wave spectral range emit the IR-radiation better and more stable.
Please note, that only the surface material is the crucial factor for the emissivity, for example, lacqured, metallic objects emit long-wave very good. The same applies to oily, dirty or rusty sheets. If in doubt, you can apply our emission factor spray item no. 03304 or you can make a comparison measurement with a digital Thermometer (for example MP2000 – Article No. 3740300) and contact sensors.
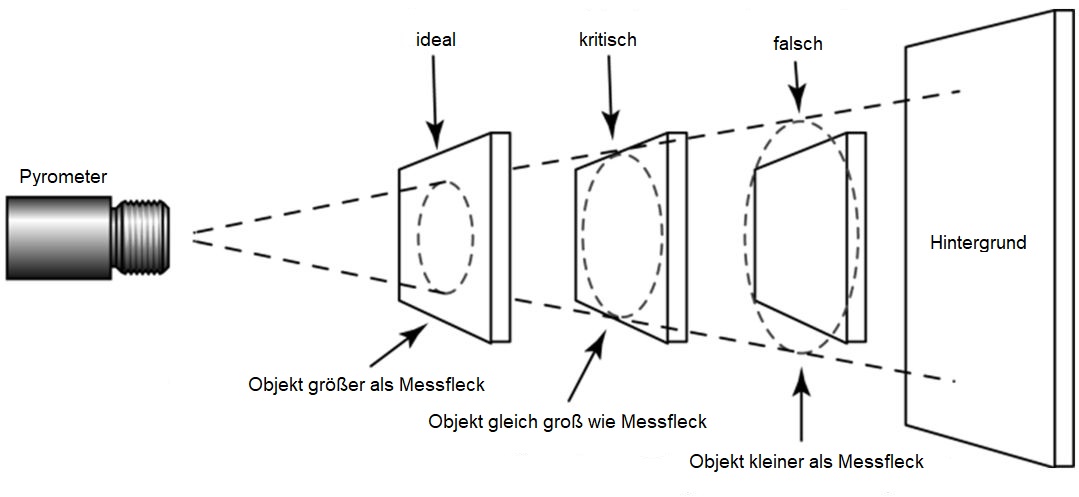
The measuring spot
Depending on the distance, the optical system of a radiation pyrometer form a measuring spot on the measuring object. For the measuring signal, the IR-irradiation will be analysed. Choose the measuring distance so, that the measuring spot in size is always less than the measuring object itself. Otherwise the background radiation measurement can distort the measuring result.